Brokerdealer.com blog update courtesy of the Wall Street Journal.
Brokerdealer.com blog update courtesy of the Wall Street Journal.
Venture capitalist and Benchmark partner, Bill Gurley, advised people against “cramming” too much money into startups, such as Uber, Snapchat, and WeWork, at last week’s Goldman Sachs technology conference. Following his speech, Gurley gave even further insight to investing in startups and how the slang word, FOMO, plays into investing.
After speaking about the risks of “cramming” too much money in startups at the Goldman Sachs technology conference last week, venture capitalist Bill Gurley exited the stage.
More than a dozen investors swarmed the lanky partner of Benchmark, eager to speak with him— but few were planning to heed the venture capitalist’s advice. According to Gurley, one man, who represented a large mutual fund, asked, “You don’t want us to invest in this but the big tech stocks are not delivering enough growth and my competitors are getting into these startups, so what are we supposed to do?”
Gurley says he didn’t have a good answer but he wasn’t surprised by the sentiment, which he describes as FOMO, a slang popular among millennials that stands for “fear of missing out.”
It is this infectious FOMO, according to Gurley and other venture capitalists, that has created a flotilla of billion-dollar startups with ever-soaring valuations and mixed financials.
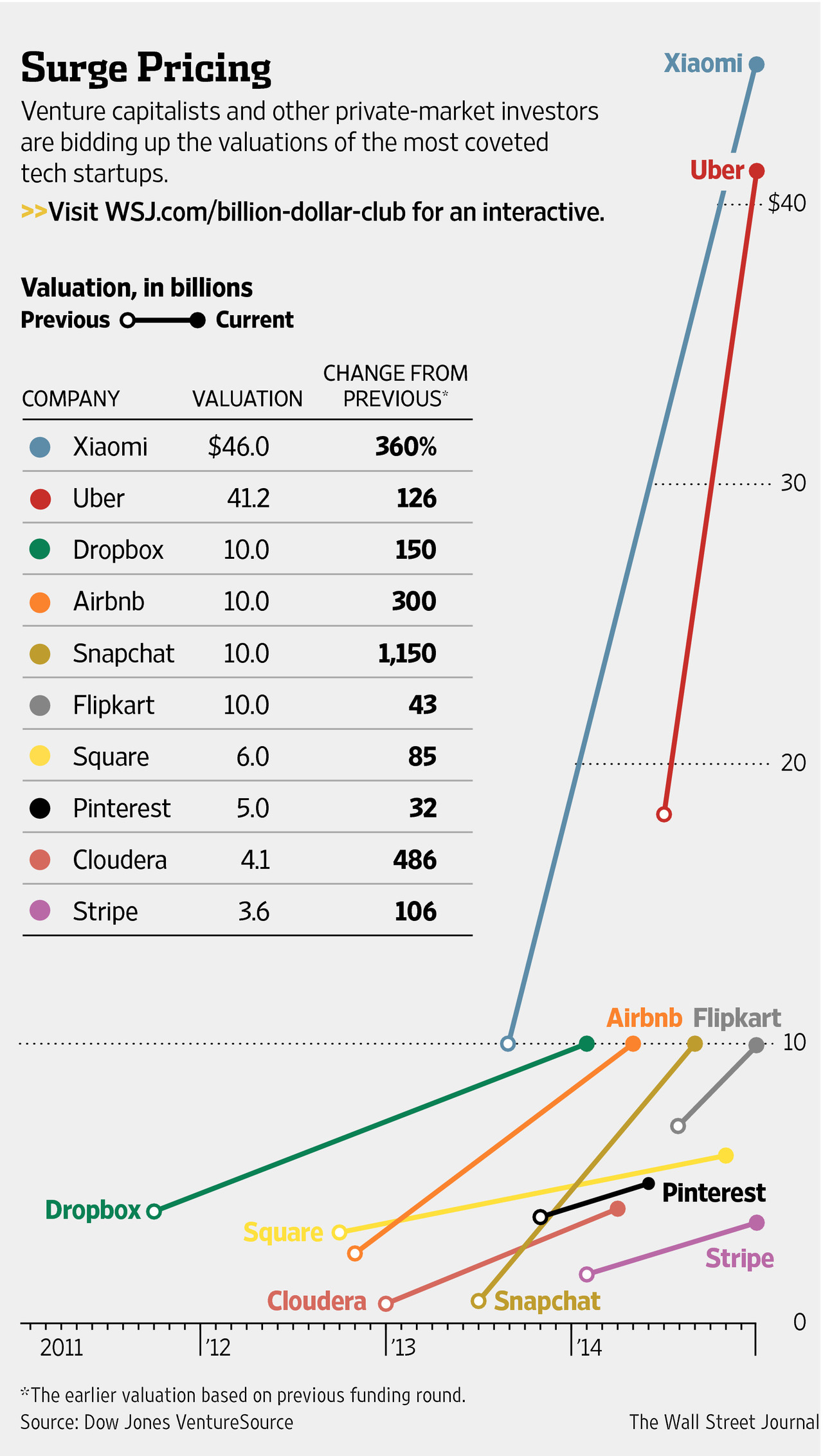
According to The Wall Street Journal’s Billion Dollar Startup Club, there are now at least 73 private technology companies worth more than $1 billion dollars, versus 41 a year ago. Some, such as Uber, the $41.2 billion car hailing app backed by Gurley’s Benchmark, are worth enormous sums. At least 48 companies were valued at $1 billion or more for the first time, and another 23 members moved up the ranking after raising more money.
Many investors are treating these 73 companies as if they were publicly traded, says Gurley. They are investing sums of money usually reserved for IPO offerings and, sometimes, giving away those dollars with the kind of confidence usually associated with investors who’ve perused regulatory filings for detailed financial information. The investors themselves are a blend of traditional venture-capital players and typically public-market investors: hedge funds, mutual funds and banks. They are sort of meeting in the middle, with the venture capitalists investing in later-stage companies than they have historically done, through new growth funds, and the institutional investors getting in before the IPO.
“We’ve been calling this the private-IPO slice,” said David York, managing director of Top Tier Capital Partners, a fund of funds. “The valuation of risk is a public-market thought process versus a private-market thought process.”
Gurley, who has become a vocal critic of irrational behavior in the industry, says he’s also very worried about the pile-up in the “private IPO” market.
He’s worried that venture capitalists’ new bedfellows, such as mutual funds, are too new to venture capital to properly weigh the risks and realize that these billion-dollar companies are not guaranteed home runs.
“This replaces the IPO — but not all these companies are IPO level candidates,” he said. “Would you hand a teenager $200,000?”
According to data collected by The Journal, of the 29 firms that have invested in five or more current billion-dollar startups, only about half are traditional venture-capital firms. The rest are a mix of institutional investors, such as the Dragoneer Investment Group and Tiger Global Management, and strategic investors, such as Intel and Google. Near the top of the list is Tiger with 12 investments in private billion-dollar companies, and T. Rowe Price Group with 11. In this group, Tiger also raised the most money last year, keying up $4 billion, or 12% of all venture capital raised in 2014.
With such financial heavyweights jumping in, many of their peers are wondering: Can I afford to sit out?
It’s difficult to quantify exactly how much money is sloshing around at this level. Several top venture capital firms have raised large growth funds in the past few years, but total contributions from hedge funds, mutual funds and banks is practically immeasurable without knowing how much each invested in particular funding rounds. Whatever the amount, this layer of growth capital could warp prices, venture capitalists say.
“It’s like traffic on the highway, you add just 5% more cars and it slows down traffic considerably,” said Glenn Solomon, a managing partner at GGV Capital. His firm is an investor in four companies in The Billion Dollar Startup Club.
In some ways, Gurley’s firm has benefited from this influx of pre-IPO capital. His firm is an early investor in four companies in the Billion Dollar Startup Club: Uber, Snapchat, WeWork and Jasper Technologies. All four have since raised money from a big public-market investor.
For the entire article from the Wall Street Journal, click here